Part 4 - Introducing permissioning - Wiki OpenEthereum Documentation
Up to now, anybody with the encrypted Document and the Document key id could have access to the decryption key as the Secret Store configuration files specify acl_contract = "none".
To verify this, let’s suppose that Charlie intercepted the email in which Alice sent the encrypted document to Bob along with the Document Key id.
1. Sign the Document key id with Charlie’s account
Just like we did for Alice and Bob, as a mean to sign our messages, we need to first sign this Document key id with the address of Charlie.
Using secretstore_signRawHash:
curl --data-binary '{"jsonrpc": "2.0", "method": "secretstore_signRawHash", "params": ["0xdab0055e3abb40d7281b058bb5e6966c50582951", "charliepwd", "0x45ce99addb0f8385bd24f30da619ddcc0cadadab73e2a4ffb7801083086b3fc2"], "id":1 }' -H 'content-type: application/json' http://127.0.0.1:8545/
0xdab0055e3..966c50582951is Charlie’s address (created in Part 1)charliepwdis Charlie’s password0x45ce99addb..083086b3fc2is theDocument key idgiven by Alice to Bob and intercepted by Charlie.
The result is the signed Document key id with Charlie’s account.
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"result": "0x0183e3274d2bde058c881e347e95a489e5ae85a3ca530376c2891adfe7aa92462af43e72450552208cc1e73404f354af5cdb7927f85c866dbfc3edf4f40b7acf01",
"id": 1
}
2. Ask the Secret Store for the decryption keys
Charlie can now call the Secret Store to retrieve the document’s keys.
curl http://localhost:8010/shadow/45ce99addb0f8385bd24f30da619ddcc0cadadab73e2a4ffb7801083086b3fc2/0183e3274d2bde058c881e347e95a489e5ae85a3ca530376c2891adfe7aa92462af43e72450552208cc1e73404f354af5cdb7927f85c866dbfc3edf4f40b7acf01
http://localhost:8010: is the address and port at which SS1 exposes the Secret Store HTTP API;45ce99addb..3086b3fc2: is theDocument key id;0183e3274d..40b7acf01: is the signedDocument key idgenerated in the previous step;
Charlie receives as a result the triple (decrypted_secret, common_point, decrypt_shadows):
{
"decrypted_secret": "0x473fb1fae08d889bd6f3b552990bef1f61997b21c4dfec3140c63c42a4289b59b8f9824fad3d35400e1f3acd8bc15b4b80ea5ca55037a83f24a1e1d5c86cfc61",
"common_point": "0xf0e62b05b68b1847ad948572a1b04a91dee7d7dca2f675fd00c136eb706d4916fb1fcdd446ab9df236eba3ab8d6184b7b3f4e8584259b5e2dc6dff8bcb07c632",
"decrypt_shadows": [
"0x04710be8785baca46e49e36cc0b9bc8ed4a5fda626820e85b442bf19f50188fea5f0d7e6e3bb5c94a7dd57e53aa3695630e81beb6c345d9d590454ffc167a7917b4b15fd5023ee4f2c55939169bad88284dd6ed95c113da446a35fa8794c6d94398ef0725b9197612e7b4a093390ea36cdadf7b246de76133c38990d346270d55a5cc91f9ff609a33ab7220cef15a791b0",
"0x04157eb5523a6c781ffce7a557aa04f3e5cefe5af3e2f3561f5be7639ef592ae13f1739706a02bc68d4338a55e4fb66cf02928766bea303467f653c3e15152bc3e7e833f72cc476789c00c19ce438a364aae998320703e5ee404fd32d799eae17c25ad7b487f85bcc2b1998cda1cc23e7c4580e4ec1ee7ec2fdb43a004a83dd3e0d3976e6a3d843081549809d06fd38331"
]
}
This is expected, but annoying as Alice would like to make sure that only Bob can decrypt and read this document. We will need to setup a permissioning contract to make sure that only selected accounts can access these keys.
3. Create and deploy a Permissioning contract
As explained in the Secret Store documentation, a permissioning contract can be deployed and specified for the nodes to verify the permission of the keys requester.
To deploy and test the permissioning contract, we will use http://remix.ethereum.org connected to our local client running with the users.toml configuration as it uses standard ports. We will unlock Alice’s account so that it can be used to deploy the contract.
To allow Remix to access our node from the browser and deploy a contract, we need to enable the eth and net JSON-RPC HTTP API as well as specify the CORS header for remix.
To do so, modify the [rpc] and [account] section of users.toml to have the following:
[rpc]
port = 8545 #default http port for RPC
apis = ["secretstore","eth","net"] # add "eth", "net"
cors = ["http://remix.ethereum.org"] # allow remix to access this node
[account] # unlock Alice's account to deploy the contract
unlock = ["0xe5a4b6f39b4c3e7203ca8caeecbad58d8f29b046"]
password = ["alice.pwd"]
As you can see, you will need a file with Alice’s password, that you can create on with the following command (linux):
echo "alicepwd" > alice.pwd
The full users.toml file is accessible here.
In this tutorial, we will use a trivial contract that will answer true if the user willing to access the keys is Alice or Bob, and if the document requested is the Document key id chosen by Alice. Any other requester or any other document would result in false. To deploy the contract head to http://remix.ethereum.org.
The permissioning contract looks like:
pragma solidity ^0.4.11;
contract SSPermissions {
bytes32 documentKeyId = 0x45ce99addb0f8385bd24f30da619ddcc0cadadab73e2a4ffb7801083086b3fc2;
address alice = 0xe5a4b6f39b4c3e7203ca8caeecbad58d8f29b046;
address bob = 0xfeacd0d28fd158ba2d3adb6d69d20c723214edc9;
/// Both Alice and Bob can access the specified document
function checkPermissions(address user, bytes32 document) constant returns (bool) {
if (document == documentKeyId && (user == alice || user == bob) ) return true;
return false;
}
}
- In Remix, create a new file by clicking the
+at the top left. - Name it as you wish and paste the code of the contract.
- Make sure to edit it to use your own addresses and
Document key id. - On the right side select the tab
Run. - Make sure you have a node running with
users.toml. - Select in the Environment drop-down menu
Web3 provider. - Use the default “http://localhost:8545” as it is the port selected in
users.toml. - Select Alice’s account in the next drop-down.
- Click Deploy.
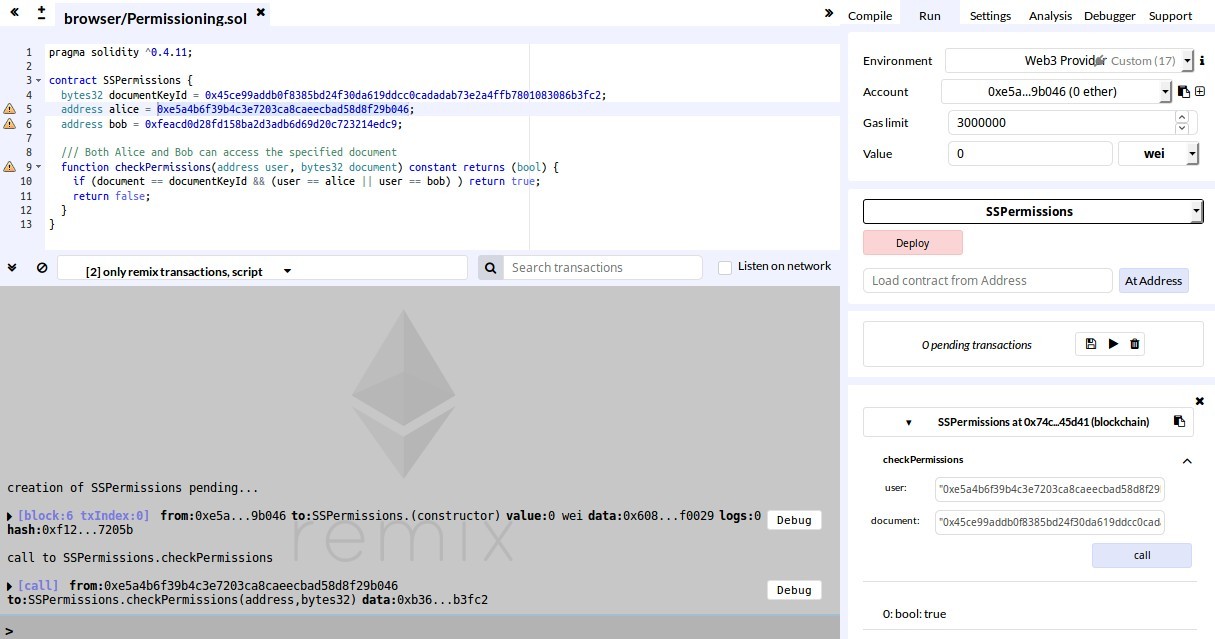
- On the right side, you will be given the address of the contract that you can copy.
- You can also test your contract right away, in the screenshot above, I verified that Alice can access the keys.
4. Modify the Secret Store configuration files
Now that we have the contract deployed on the dev chain, we can specify it in the Secret Store nodes.
Add the acl_contract parameter of the [secretstore] section of each Secret Store node (ss1.toml, ss2.toml, ss3.toml) as follow:
acl_contract = "74c369bf541131062ad208576e40aa258ff45d41" instead of “none”
The full configuration files are accessible here.
5. Permissioning verification
Make sure that all the Secret Store nodes were updated with the address of the contract and relaunched. You should see that the message warning about the permissioning has now gone.
5.1 Test with Bob
You can now make sure that Bob still has access to the keys by repeating the call made in Part 3
curl http://localhost:8010/shadow/45ce99addb0f8385bd24f30da619ddcc0cadadab73e2a4ffb7801083086b3fc2/a589bebde7944fd4e01bd3a984fadb1ac0345aec445742e6ff34bb8b81cee5ba01dabfd199a3c90faea62b34051dd12f56e4af70027fd66b19e7f0038bfc158301 | jq
Bob still has access to the keys.
{
"decrypted_secret": "0x80bcbbc44eac48b1b861736734f9a1139b0ebf5244819351ae246a12ef424184e789d8a61726689529d3291bd599f7140eec14e4c3e6e34e90a4d2daf6737736",
"common_point": "0xf0e62b05b68b1847ad948572a1b04a91dee7d7dca2f675fd00c136eb706d4916fb1fcdd446ab9df236eba3ab8d6184b7b3f4e8584259b5e2dc6dff8bcb07c632",
"decrypt_shadows": [
"0x04aec0589e3f9541b77e26d2e25b0a7f8d44838d47a0859f62385cdd29d9c053b99fc91683d70a4b7e2542ecf7516046a461f5b49dc65af143948ebde954ea3621ff17972eaa916366ff0595043ca08fd881747575872b8248b6a9189e2a289a3d69374c863a0bda9e06c9e69b9dc687d6a32b6d04ed2676f482ec423e3976bcb47ba14af2560738a8fa6c83f2b48c3e94",
"0x04ee25dd56054044879f32db82058c223cc16794f4cad55889e5f35ca2b1875d51f7cc2fe0beb669c17a1b5781718ebf0eefc896a62e3631e7f4a0497e639cd0b7059993c56b730ae38e4a2340d04233008c6913b1c1da3e086ff4321e3d7a057adbfc0bbd42ba5422c6b33994fd25ffa5dd88bb5dc515c84bd579f3d30f895a3c3a86c62a5afc904e479fce3fd831ebb8"
]
}
5.2 Test with Charlie
We can repeat the call from Step 2 to see if Charlie has access to the keys:
With the -i option to curl to see the HTTP headers.
curl -i http://localhost:8010/shadow/45ce99addb0f8385bd24f30da619ddcc0cadadab73e2a4ffb7801083086b3fc2/0183e3274d2bde058c881e347e95a489e5ae85a3ca530376c2891adfe7aa92462af43e72450552208cc1e73404f354af5cdb7927f85c866dbfc3edf4f40b7acf01
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
Content-Type: application/json
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Date: Thu, 28 Jun 2018 16:06:44 GMT
"\"Consensus unreachable\""
Charlie gets an HTTP Header 403 forbidden, he can not access the keys.
| ← Part 3 - Key retrieval |